Optipedia • SPIE Press books opened for your reference.
Distortion
Excerpt from Field Guide to Geometrical Optics
Distortion occurs when image magnification varies with the image height H. Straight lines in the object are mapped to curved lines in the image. Points still map to points, so there is no image blur associated with distortion.
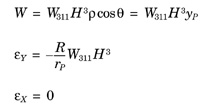
Distortion is a quadratic magnification error, and the image point position is displaced in a radial direction. The figures assume H represents a positive image height.
Barrel distortion
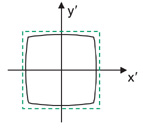
Barrel distortion results when the actual magnification becomes less than the paraxial magnification with increasing H. The corners of a square are pushed in towards the optical axis.
Pincushion distortion
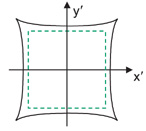
Pincushion distortion results when the actual magnification becomes larger than the paraxial magnification with increasing H. The corners of a square are pulled away from the optical axis.
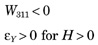
The transverse ray fans for wavefront tilt and distortion both are constant with respect to yP. These two aberration terms can be distinguished by their different field or H dependence: linear for wavefront tilt and cubic for distortion.
J. E. Greivenkamp, Field Guide to Geometrical Optics, SPIE Press, Bellingham, WA (2004).
View SPIE terms of use.

